Without a Google Search Console SEO audit, there is no way for your SEO efforts to improve.
Hence, today, it is one of the most important steps of an SEO strategy.
From content issues to technical aspects, multiple factors can cause your rankings to grind to a halt.
To understand every minute detail of your website and fix the errors, today we have come up with a step-by-step breakdown of the Google site audit.
Read More: The Ultimate Guide to Comprehend Average Position in Google Search Console
What is Google Search Console SEO Audit?


Through an analysis of your website, SEO audits assess a wide range of variables that affect your website’s positioning in search engine results pages, or SERPs.
These components include your website’s technical SEO performance and on and off-page SEO.
Before we dive into the Google Search Console SEO audit, let’s go through the components of an audit in the following section.
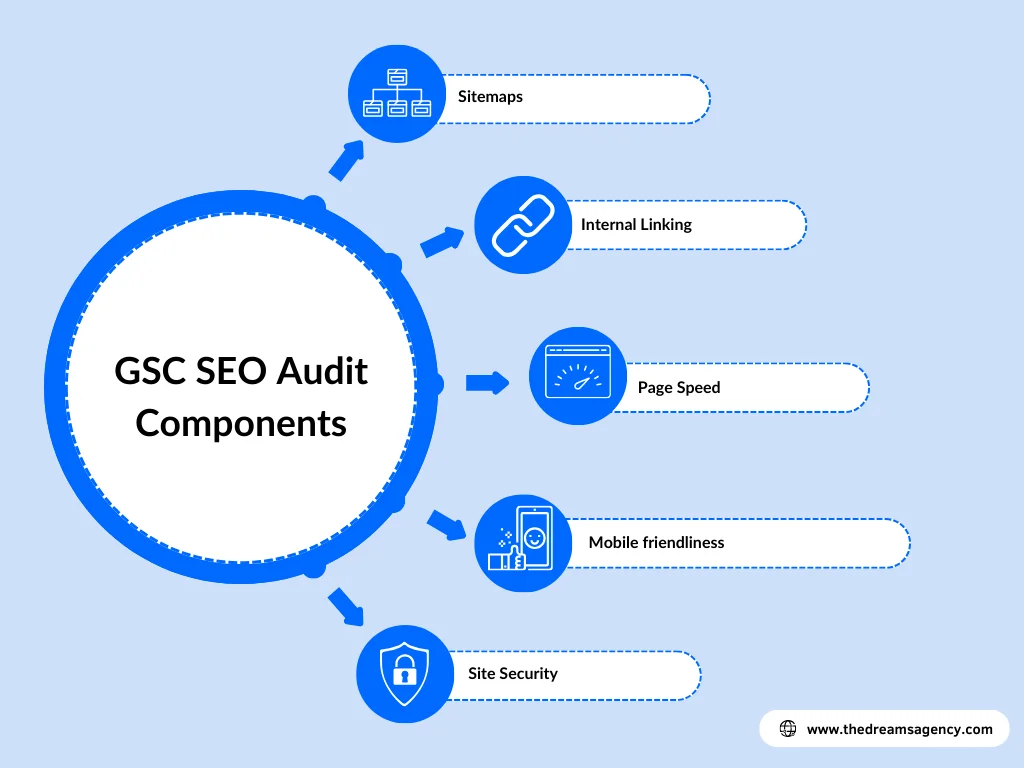
Important Components of Google Search Console SEO Audit

1. On-Page SEO
An on-page SEO Google site audit aims to optimize website aspects that affect search engine results pages.
Keyword Research to Establish a Plan
Before using any type of keyword in your content, you should know what material ranks well.
Also, you should know what people mean when searching for a particular term.
Examine the websites of your rivals that are performing well in Google and note the content strategies they are implementing.
Read our blog on the best market analysis tools to learn how the best analysis tools work.
Use of Keywords
Every effective keyword strategy has good keyword research to optimize the title tag, meta description, body content, and headers.
These provide context for the content of your page to search engine crawlers and visitors alike when they appear in the SERPs.
Through Google Search Console SEO audit, you can locate the underperforming keywords and find new opportunities to boost ranking.
As a bonus, you use the same tool for keyword research.
Internal Linking
Optimizing your website to make it easier for search engines to find the pages on it is critical to your SEO. Internal linking plays a significant role in that.
Internal links improve your SEO by making it simpler for users and search engine crawlers to find pages on your website.
Therefore, it is supposed to be a part of your Google Search Console SEO audit.
Read More: A Beginner’s Guide to High-Quality Link Building
Sitemaps
Sitemaps provide search engine crawlers with a means of navigating your website’s pages.
Search engines are the only users of XML sitemaps. They work incredibly at assisting search engines in finding new pages to crawl.
Google Search Console can crawl an XML sitemap once you submit it.
2. Off-page SEO
The SEO components you can affect but do not directly control make up off-page SEO.
Backlinks to Bring Traffic
As part of the Google Search Console SEO audit, you should also be aware of the backlink profiles of your competitors and yourself.
3. Technical SEO
Page Speed
During your Google Search Console SEO audit, you can use Google’s free PageSpeed Insights tool to assess the performance of your website.
This tool will tell you how well your website loads on desktop and mobile devices and provide recommendations for resolving any issues.
Mobile-Friendliness
Additionally, Google has added a new ability to the Google Search Console that lets you determine whether your website is optimized for mobile devices.
Site Security
One aspect of SEO ranking is site security. So, you can’t ignore it while conducting a Google Search Console SEO audit.
A secure website lets users know they can trust you by encrypting and safeguarding their personal information.
Read More: Mastering SEO in 2023
10 Necessary Steps For Google Site Audit


Step 1: Set Up An Account
Establishing a Google Search Console account is the first step. Visit the Google Search Console page and log in with your Google account if you haven’t already.
After logging in, select Add Property and proceed with the procedures to validate your website.
There are other ways to validate your website, such as uploading an HTML file to the root directory of your website or placing a verification code in the header of your website.
Google’s database does not contain pages that are not indexed. They are not ranked by Google.
Use Google Search Console to immediately check for problems to determine if your pages have been indexed.
Navigate to the Pages report located in the Index part of the menu on the left.
You will find a number of reasons causing indexing issues. Thankfully, Google offers solutions and answers to all these issues.
Go over each of the reasons one by one.
It is okay if 20% of the site is not indexed. Such URLs include:
- Redirected pages
- Admin Pages
- Different pages using the canonical tags
- Feed pages
If you discover a page that is supposed to be indexed but isn’t, take Google’s instructions to rectify the problem. Press the Validate Fix button when finished.
With a Google Search Console SEO audit, you can also identify several technical SEO and indexing problems.
Search through your website and select the Issues option.
These are all the mistakes, alerts, and notices impeding the SEO performance of your website.
Now, to view only indexing concerns, choose Indexability from the Category dropdown menu.
Step 2: Check For Issues That May Lead to Penalties
Security concerns should be addressed immediately as they are an obvious cause for concern.
The section about security and manual actions can be found by scrolling down.
These are penalties that Google’s human reviewers have assigned to your website.
Google may flag and have a real person review the website if it finds that you have broken the conditions of use.
Algorithmic penalties, in which a website’s rating declines due to automatic algorithm changes, are not the same as manual actions.
That is because the human resources from the Google team don’t have the power to lift this penalty.
Manual actions preserve the calibre and applicability of search results by ensuring that websites adhere to Google’s rules and refrain from manipulating search rankings.
Among the things that can cause you to be flagged are:
- Black hat linking
- Spamming
- Link cloaking
- Malware/hacking
You should give this your top priority right away if you click through to these areas and notice that there is a detected issue.
Otherwise, your site’s rankings may drop significantly, and traffic may drastically decline.
Step 3: Look for Issues with Mobile-Friendliness
One of Google’s primary Page Experience indications is mobile friendliness.
The Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability report allows you to look for any problems.
Simply select Mobile Usability from the menu on the left under Experience.
In this step of the Google Search Console SEO audit, you will see a brief summary of your pages’ usability over time.
The report offers a list of all the problems with mobile friendliness.
Each issue can be expanded to view every page that is impacted.
To resolve the problems, according to the guidelines provided in Google’s Search Console Help Center.
After you resolve the problem, you may verify the change to ensure Google reevaluates the page and marks the problem as fixed.
Step 4: Evaluate the Core Web Vitals Report
Three crucial metrics comprise Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): The longest time it takes for the largest piece of content or image to load.
First Input Delay (FID): The amount of time it takes after a click for a website to load and start interacting.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): The quantity of unanticipated layout changes that occur while the page loads.
Core Web Vitals show how quickly the page loads, how interactive it is, and how stable its appearance is.
The average page load time in 2023 was less than 2.5 seconds.
To determine which of your pages may effectively meet this criterion, you can use this report.
In Google site audit, you will get a number of pages that require improvements.
Step 5: Identify Underperforming Keywords
Google Search Console keeps track of your keywords’ present rankings.
These insights can be used to identify the keywords that are about to take up prominent SERP positions.
Your traffic will increase with only a small amount of work put into optimizing these pages.
Go to Performance > Search results, enable Total impressions and Average position and then scroll down to the table of queries.
Create filters to display keywords that are not performing well. Depending on your approach, click filter > position > greater than and enter 3 or 10 as the cutoff point. Based on impressions, you can filter the keywords.
There isn’t much to gain from shifting a keyword to a better position if it is now in position 5 and receives 20 impressions per month.
Search Console now provides you with a list of underutilized terms with the most potential. To view the pages that rank for a given query, click on it and then choose Pages.
Step 6: Find Outdated Pages
As time passes and a page becomes old, it is normal for it to lose traffic.
Navigate to the Search Console results page.
Select Date and Compare the recent six months to the prior period to determine which pages require an update.
Turn on Clicks, then navigate to Pages to find out which pages lost the most visitors in the previous six months.
The decrease in traffic may indicate that the website needs some new changes.
Examine the page to ensure the content is still accurate, and put it side by side with similar pages from competitors.
This is a good way to tell whether there are enough keywords and the optimization of the headings and titles.
Step 7: Assess the On-Page Performance of Your Website
Using the performance report from Google Search Console SEO audit is one of the finest strategies to enhance your website’s ranking in organic search results.
Click the Performance option in the menu to view this report.
The performance report will display the overall click-through rate, impressions, average click-through rate, and average ranking position for your website on Google.
You can tap on the Export button at the top right of the report to export the full document as an Excel file, CSV file, or Google Sheets so you can analyze the data.
Step 8: Check the Crawlability of the Site
Google Search Console SEO audit verifies if your pages are crawling on Google.
Navigate to Crawl Stats in Settings.
You may see how frequently Google crawls your website by opening that report.
Google should crawl your website more often if you’re publishing new information on a regular basis.
This section explains which pages are not being crawled and why.
Remember that errors in the Search Console will negatively affect your site’s crawlability. Don’t let them build up.
There are two primary kinds of errors you will find in this Google Search Console SEO audit step:
404 errors: These occur when Googlebot crawls a link, but the website is no longer accessible. A simple error or altering a page’s URL without first redirecting traffic can cause this.
500 errors: These indicate server problems. Hence, verify that your code does not contain them or exceptions.
Moreover, Robots.txt can be used to identify and remove pages that you do not want Google to crawl.
The robots.txt file is a straightforward text file stored in your website’s root directory. It tells web crawlers what areas of your website they can and cannot access.
You must log into your hosting account and go to the root directory in order to accomplish this. After that, you may add a disallow code to the robots.txt file with the URL you want to block.
After that, use GSC’s search feature to confirm if a page is not being crawled.
You will see the result after entering the URL.
Step 9: Recognize Security Issues
Do you agree that the audience should feel comfortable sharing sensitive information on your website, like credit card numbers or email addresses?
Then, make sure you follow this Google Search Console SEO audit step to check if your website is using the https or secure protocol.
To accomplish this, your website must have a working SSL certificate, and all HTTP versions of your pages must point to https versions.
Once again, for this Google Search Console SEO audit step, go to the Page Experience section under the Experience tab.
You should think about switching to the protected version of your website if it isn’t already using the https protocol.
Step 10: Examine the Links on Your Website
The last step of the Google Search Console SEO audit is reviewing backlinks and internal linking on your website.
For Backlinks
Click Links from the navigation menu to open Google Search Console’s backlinks report.
The links that Google has found connecting to your website from other domains are displayed in this report. You need to look in the External Links column.
Things you will discover from the report:
Top connected pages: the pages on your website with backlinks are displayed in this section.
Top linking sites: the external domains that backlink to your website are displayed in this area.
Top linking text: the clickable text, or anchor text, used in the backlinks is displayed in this section.
Utilize the Export External Links button in the report’s upper right corner.
You should review the list after exporting the file to a spreadsheet and mark any backlinks that seem to be:
Spammy: The usage of anchor text or the domain name itself may be questionable or spammy.
Beyond the niche of your website: Although there won’t always be a problem or error with this, make sure to mark any of these backlinks and consider why you could have gotten them.
Purchased: Purchasing backlinks is seen as a black hat link-building strategy against Google’s guidelines.
For Internal Links
The Internal Links column in Google Search Console’s Links section provides information about the internal links used on your website.
To get to the internal links part of the links report from Google Search Console, click More after swiping down to view the full list.
A page should generally have more internal links connecting to it, and the more essential it is.
Examine the internal linking report on your website and:
Add more internal links to any significant pages you discover that don’t already have enough of them.
Look for any less significant pages with many internal links going to them and think about eliminating some of them.
By following this step of the Google Search Console SEO audit, you can work towards building the credibility of your site.
FAQs
What makes a Google site audit crucial?
An SEO audit is crucial since it highlights any website’s SEO issues, allowing you to fix them and start ranking higher.
Why competitor analysis is important for Google site audit?
To defeat the competition and learn the best SEO tactics to implement in your strategy, competitor analysis is necessary.
Final Words
By conducting a Google Search Console SEO audit, you can understand your strengths and weaknesses, improve rankings, and sharpen your SEO techniques.
To get expertise for the SEO of your website, you can invest in SEO experts rather than tools. These experts have knowledge and are equipped with several SEO tools to deliver the best results.


